Process Improvement
Process Improvement
Process improvement is for any business looking to stay competitive and efficient. Analyzing and optimizing your workflows can reduce waste, increase productivity, improve safety, and improve your bottom line. Our experts can help you identify areas for improvement and implement effective solutions that will take your business to the next level.
KPC's approach to process improvement begins with understanding how your organization makes money, the challenges it faces, and the goals it wishes to achieve. Every business is unique, so we don't offer one-size-fits-all solutions.
By relying on the proven principles of the Lean Enterprise, Lean Six Sigma, and our extensive experience in leading manufacturing businesses, our consulting method is an efficient, results-focused approach. We understand you have to balance running a business and improving it simultaneously. We know that every company starts from a different point, so we meet you where you are and customize our approach to maximize your short and long-term goals.

Our process starts with upfront alignment interviews and often an on-site assessment to determine your business goals, where you are starting from, and the improvement opportunity. From there, our team puts together a customized roadmap that typically includes the following elements:
- Staff Training
- Process Improvement Facilitation (i.e., kaizen events, A3’s, etc…)
- Lean Leadership Development (teaching and coaching leaders how to lead in a lean environment)
- Gamification (systems to engage your team in making daily improvements easy, fun, and rewarding)
- Identifying and confirming Key Performance Metrics
- Regular Progress Reviews (ensuring we are moving the metrics in a positive direction and changes are sustainable)
Common Countermeasures Used in our Improvement Process
5S
Eliminates process waste due to a poorly organized workspace (e.g., looking for tools, materials, and information to perform a task.
Visual Factory
Using charts, boards, screens, infographics, and icons to convey needed information about a process to operators and leaders.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping is a visual tool that maps the production flow. It shows the current and future state of processes in a way that highlights opportunities for improvement.
Process Waste Reduction
Process waste does not add value from the customer’s perspective.
Continuous Flow
Continuous Flow occurs when work-in-process smoothly flows with minimal buffers between steps of the manufacturing process.
Root Cause Analyses
Root Cause Analysis is a systematic problem-solving approach focusing on resolving the underlying cause of a problem instead of applying quick fixes that only treat immediate symptoms of the problem.
Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing)
Installing methods of detecting and preventing operator errors that result in product defects.
Standard Work
A living document prescribing the most efficient sequence of job tasks (including the time required for each, safety precautions, and quality checks).
Hoshin Kanri
A strategy management process designed to align company strategy with tactics to ensure strategy execution.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
An advanced holistic approach to equipment maintenance focusing on preventive and proactive practices to improve equipment reliability.
Process Layout
Plant and process layouts combining processes horizontally across the factory vs. vertical process departments like silos in a traditional facility layout.
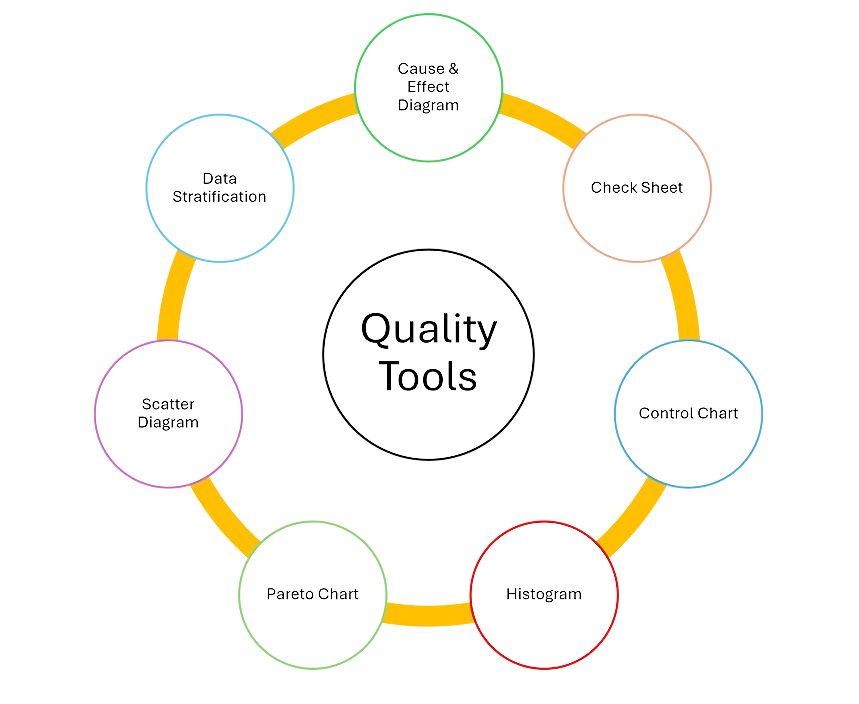
Seven Basic Quality Tools
The wise use of these quality tools enables the effective management of product and process quality, no matter what industry you serve.
Setup Reduction (SMED)
Single-Minute Exchange of Die reduces setup (changeover) time to less than 10 minutes. SMED techniques include:
- Converting setup steps to be external (performed while the process is running)
- Simplifying internal setup (e.g., replace bolts with knobs and levers)
- Eliminating non-essential operations
- 5S Workspace
- Creating Standardized Work instructions
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Provides a practical framework for measuring productivity at the machine level. The components of machine effectiveness include:
- Time available to run
- Ability to run at the required rate
- Ability to produce defect-free products while running at the required rate
Bottleneck Analysis (TOC)
Identifies the constraint of the manufacturing process limiting its overall throughput, improves the contracting performance, and balances the whole process around the constraint.
Kaizen
A systematic approach involving all employees in gradually improving operations and processes. Kaizen is often considered a "building block" of lean production methods and is recognized worldwide as a key part of an organization's long-term competitive strategy.
Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA)
a four-stage, iterative problem-solving model favored to manage and improve processes and products. It's also known as the Deming wheel or cycle, the Shewhart cycle, or the control circle.
- Plan: establish the plan and expected results
- Do: implement the plan
- Check: verify expected results achieved
- Act: review and assess; do it again
Take Action Today
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Contact us today with any questions!
Contact Us
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Key Performance Consulting so popular?
Key Performance Consulting has earned its popularity through our exceptional business consulting services tailored specifically for small and mid-sized organizations. Based in Charles City, we are dedicated to helping businesses achieve enterprise excellence by providing customized training, coaching, and consulting offerings. Our approach to business consulting services involves understanding how your organization makes money, the challenges it faces, and the goals it strives to achieve. With a unique blend of Lean Enterprise, Lean Six Sigma, and our extensive manufacturing experience, we provide results-focused business consulting services that help you reduce waste, enhance productivity, and improve your bottom line. Standing out in Charles City, our business consulting services empower your organization to stay competitive and efficient. Experience the difference in our business consulting services today with Key Performance Consulting and elevate your business to new heights.
Where can I find business consulting services in Charles City?
If you are searching for top-tier business consulting services in Charles City, look no further than Key Performance Consulting. We pride ourselves on providing comprehensive solutions tailored to meet your organization's unique needs. Our expert team stands ready to help streamline and optimize your business operations. Let's discuss how we can assist your company!
What are the benefits of process improvement in business?
Process improvement is crucial for any business looking to stay competitive and efficient. By analyzing and optimizing workflows, businesses can reduce waste, increase productivity, enhance safety, and ultimately improve profitability. Key Performance Consulting specializes in identifying improvement opportunities and implementing effective solutions. Discover the advantages of enhancing your processes with us!
How can lean leadership development benefit my organization?
Lean leadership development teaches and coaches leaders to efficiently manage a lean environment. This expertise fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling your organization to operate more efficiently and achieve long-term success. At Key Performance Consulting, we provide the support and resources necessary for developing effective lean leaders. Transform your leadership approach with our expert guidance!
What is Value Stream Mapping, and how does it help my business?
Value Stream Mapping is a visual tool that allows you to map the production flow and highlight improvement areas. It helps businesses identify inefficiencies, streamline operations, and increase productivity by providing a clear view of current and future states. Enhance your business processes with Key Performance Consulting's expertise in Value Stream Mapping. Contact us today for more details!
Why choose Key Performance Consulting for staff training?
Our staff training programs are designed to equip your team with the skills and knowledge necessary for achieving continuous improvement and operational excellence. By tailoring our training initiatives to your specific organizational needs, we ensure impactful outcomes. Let Key Performance Consulting empower your workforce for better performance. Get in touch to learn more!

